Arthritis Basics: What It Is and How to Treat It
Introduction to Arthritis
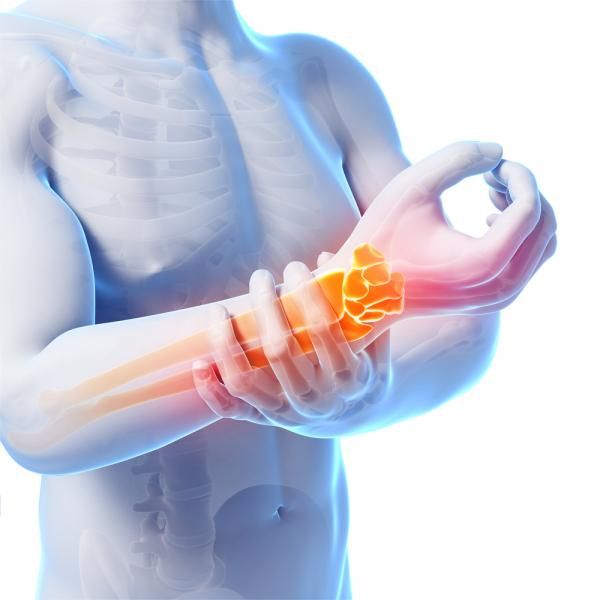
What is arthritis?
Arthritis is a condition that produces pain, swelling, and stiffness in joints. It renders daily activities more difficult and restricts physical movement. It can develop in one or multiple joints and occurs frequently in older adults, but it can happen at any age.
Arthritis affects the daily routine by limiting mobility, making it difficult to walk, bend, or lift. Arthritis pain can become exacerbated when muscles near the joints weaken or become inflamed. The condition is directly associated with muscular system issues and is among the prominent prevalent diseases of the skeletal system.
Knowing the Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal system is composed of muscles, bones, joints, tendons, and ligaments. The muscular system enables the body to move through contracting and relaxing muscles. The skeletal system gives the body structure and support, defending internal organs and attaching with muscles for movement.
These two systems work together. When they are healthy, your body can move easily and handle daily physical activity. However, any damage or stress to these systems can lead to acute musculoskeletal pain and reduce your flexibility and strength.
Types of Arthritis
There are many forms of arthritis. The most common types include
- Osteoarthritis: It is caused by joint wear and tear over time. It commonly affects the elderly and leads to pain and stiffness in the joints.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: It is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system targets the joints mistakenly, leading to inflammation and persistent damage.
- Gout: A form of arthritis triggered by a deposition of uric acid crystals within the joints, commonly in the big toe.
All these are under the category of prevalent skeletal system diseases. All the types impair mobility and also cause pain in adjacent muscles, resulting in muscular system health issues later.
Arthritis Symptoms
Arthritis symptoms may vary depending on the type but may include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Stiffness, particularly in the morning
- Redness or heat around the joint
- Restricted range of motion
On occasion, the joint issues result in acute musculoskeletal injury, particularly when attempting to move despite pain. Long-term harm and loss of function may result from disregarding these symptoms.
Seek medical attention when the symptoms disrupt normal life or persist despite rest and general care.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are a number of identified causes and risk factors for arthritis:
- Age: The risk grows with age.
- Genetics: A history of arthritis in your family increases your risk.
- Injuries: Prior acute musculoskeletal injuries can cause joint issues.
- Autoimmune illnesses: They cause the body to attack healthy tissue.
- Weak muscular support: Weak muscles can put more stress on the joint and enhance pain.
Neglect and improper management can worsen muscular system health issues and add to joint stress.
Treatment Choices for Arthritis
A. Home and Lifestyle Care
Some useful methods for controlling arthritis at home are:
- Losing excess weight to help ease joint stress
- Engaging in low-impact exercises such as walking, swimming, or yoga
- Utilizing physical therapy to enhance strength and mobility
- Using heat or cold packs to alleviate pain and inflammation
B. Medications and Pain Relief
For most, medications are a part of arthritis management. This includes:
- Painkillers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen
- Anti-inflammatory medications for swelling
- Muscle relaxants such as Pain O Soma 350 mg to relieve muscle discomfort
What is the muscle relaxer Soma?
Soma is a prescription medication that is employed to relax muscles and alleviate pain due to strains, sprains, and spasms. Soma 350 mg tablets act by influencing the central nervous system to slow down muscle activity. This assists patients suffering from acute musculoskeletal pain caused by injuries or arthritis.
Physicians can prescribe 350 mg Soma if there is evidence of muscle tension or spasms combined with arthritis pain.
Muscle Relaxers and Arthritis Pain
Muscle relaxants are involved in the treatment of arthritis when joint pain is exacerbated by muscle spasms or tension. They alleviate acute musculoskeletal pain and provide immediate relief when joints are inflamed and stiff.
Pain O Soma 350 mg relieves tension in muscles surrounding affected joints, so it’s easier to move and stretch. It should only be used under doctor’s orders. Before taking Soma 350 mg tablets, talk to a doctor regarding the optimal dosage, potential side effects, and its role in your overall arthritis management plan.
Long-Term Prevention and Management
To maintain healthy joints and muscles long-term:
- Avoid repetitive motion that overloads the joints.
- Use proper lifting and exercising techniques.
- Strengthen muscles using low-impact strength training.
- Eat a healthy diet and maintain a healthy weight.
- Pursue muscular system health issues before they become serious.
- Regular checkups enable monitoring for prevalent skeletal system illnesses.
Preventive visits can limit the occurrence of arthritis or retard its development.
When to Seek Medical Assistance
It’s necessary to visit a doctor if you have:
- Ongoing joint pain or swelling
- Sudden or severe stiffness
- Joint instability or deformity
- Features of acute musculoskeletal injuries
- No removal of pain by over-the-counter medication or rest
Prompt diagnosis and treatment can avoid permanent destruction and add quality to life.
Conclusion
Arthritis is a difficult condition, but it can be managed effectively with proper care. If treated with early intervention, lifestyle changes, and proper use of medications like Soma 350 mg tablets, then the amount of pain and disability can be reduced and mobility can be improved.
Proper care of both bone and muscle is important. Muscle relaxers such as Pain O Soma 350 mg are useful when utilized appropriately and in a responsible manner, at the direction of a prescribing doctor.


